Ensuring Electrical Safety Excellence: Transform Your Workplace with Expert Electrical Safety Audit Services

For Quick response for Electrical safety Audit in India you can mail electricalsafety@elion.co.in in or call us at 9013890526 or Whatsapp by Clicking here.
Welcome to Elion Technologies and Consulting Private Limited, your trusted partner in elevating workplace safety through comprehensive Electrical Safety Audits. Our audits have a primary focus on “Compliance with Electrical Safety Standards.” With a rich legacy since 2010, we take pride in being industry leaders in the field of electrical safety audits, driven by a team of certified and highly qualified auditors. With a collective experience spanning over three decades, our auditors come from diverse fields, ensuring a holistic approach to safety assessment.
This webpage outlines the process and importance of conducting an electrical safety audit by Elion. Electrical safety audits are critical for ensuring compliance with safety standards, identifying potential hazards, and implementing corrective measures to protect personnel and property. This audit not only helps in maintaining a safe working environment but also enhances the overall efficiency of electrical systems.
Schedule Your Audit Today
What is Electrical Safety Audit?
An Electrical Safety Audit (ESA) is a comprehensive evaluation of electrical systems to identify potential hazards, ensure compliance with safety standards, and minimize risks. It helps prevent electrical accidents, improves system efficiency, and protects lives and assets.
Electrical safety audits are systematic evaluations of electrical systems and practices within an organization. Elion specializes in conducting thorough audits that assess the safety and reliability of electrical installations. The primary goal is to identify risks, ensure compliance with regulations, and recommend improvements to enhance safety.
Get a Free Consultation
Why Conduct Electrical Safety Audit
Electrical systems are integral to modern operations, but they also pose significant risks if not maintained properly. Regular audits help:
Prevent Accidents: Identify and mitigate electrical hazards.
Ensure Compliance: Meet national and international safety standards.
Optimize Systems: Improve performance and energy efficiency.
Protect Lives and Assets: Reduce risks to personnel and property.
Case-study
Industries Served by Elion for Electrical Safety Audits
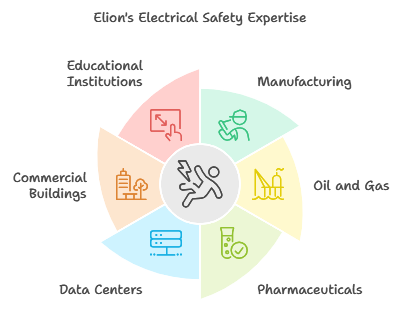
Elion Technologies proudly serves a diverse range of industries, ensuring their electrical systems meet safety standards and operate at peak efficiency. In the manufacturing sector, we help factories address risks associated with high-voltage machinery, overloaded circuits, and aging infrastructure. For the oil and gas industry, we focus on identifying potential hazards in explosive atmospheres, ensuring compliance with critical safety regulations. Our expertise also extends to pharmaceutical plants, where uninterrupted power supply and precise control systems are vital for maintaining production quality and safety.
Additionally, Elion supports data centers by preventing downtime caused by electrical faults and optimizing energy efficiency. For commercial buildings and educational institutions, we ensure safe environments for employees, students, and visitors by addressing improper wiring, faulty equipment, and emergency preparedness. No matter the industry, Elion tailors its electrical safety audits to meet specific needs, ensuring compliance with relevant regulations while prioritizing safety and operational efficiency.
Request a Quote
Electrical Safety Audit Process
1. Pre-Audit Preparation
- Documentation Review: Gather and review existing electrical safety policies, maintenance records, and previous audit reports.
- Site Assessment Planning: Develop a plan for the site assessment, including areas to be inspected and personnel to be interviewed.
2. On-Site Inspection
- Visual Inspection: Conduct a thorough visual inspection of electrical installations, including wiring, panels, and equipment.
- Testing and Measurements: Perform electrical testing to measure insulation resistance, grounding effectiveness, and circuit integrity.
- Interviews: Engage with staff to understand their awareness of electrical safety practices and any concerns they may have.
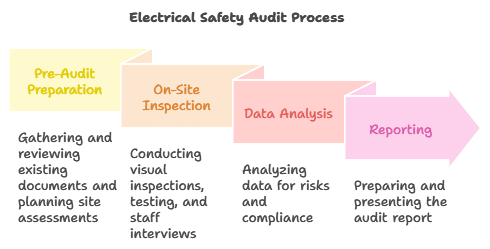
3. Data Analysis
- Risk Analysis: Analyze the data collected during the inspection to identify trends and areas of concern.
- Compliance Check: Compare findings against relevant safety standards and regulations.
4. Reporting
- Audit Report Preparation: Compile a comprehensive report detailing findings, risks, and recommendations.
- Presentation: Present the findings to management and relevant stakeholders, highlighting critical issues and proposed solutions.
Take the First Step Toward Safety
Compliance Standard of Electrical Safety Audit
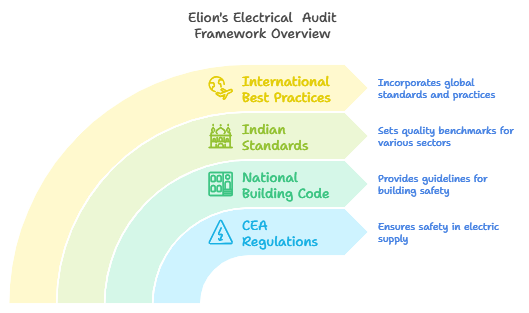
Elion’s audits adhere to the following safety and regulatory frameworks:
CEA (Measures Relating to Safety and Electric Supply) Regulations, 2023.
National Building Code (NBC) 2016.
Indian Standards (IS).
International best practices as needed.
Conducting an electrical safety audit by Elion is an essential step in safeguarding personnel and assets. By systematically evaluating electrical systems, organizations can identify hazards, ensure compliance, and implement effective safety measures. Regular audits not only enhance safety but also contribute to the overall efficiency and reliability of electrical operations.
Partner for Peace of Mind
FAQs
An Electrical Safety Audit is a systematic examination of an organization’s electrical systems, equipment, and practices to identify potential hazards, ensure compliance with regulations, and enhance overall safety.
An Electrical Safety Audit is crucial to prevent electrical accidents, ensure regulatory compliance, reduce downtime, and protect employees and assets.
Any organization that utilizes electrical systems, from small businesses to large industries, can benefit from an Electrical Safety Audit.
Regular audits are recommended, typically every 1 to 3 years, depending on the nature of your operations and regulatory requirements.
Our auditors are certified and qualified experts with over three decades of combined experience in various fields of electrical safety.
We cater to a wide range of industries, including manufacturing, construction, healthcare, technology, and more.
The duration varies based on the complexity of your facility but usually ranges from a few days to a couple of weeks.
The process includes a thorough examination of electrical systems, equipment, procedures, and documentation to identify risks and provide recommendations.
You’ll receive a comprehensive report detailing findings, recommendations, and an actionable roadmap for improving safety.
Yes, we offer consultation and support; additionally, we can help you implement the suggested safety improvements effectively.
We uphold strict confidentiality standards; furthermore, all information obtained during the audit is handled with the utmost discretion.
Absolutely, our audits ensure that your organization not only adheres to relevant regulations and standards but also helps you maintain a strong position in compliance.
We leverage cutting-edge software for simulations and analysis; consequently, this enables accurate hazard identification and risk assessment.
We strive to minimize disruptions; moreover, we can often conduct audits during off-peak hours to ensure minimal impact on your operations.
Yes, we can tailor our services to accommodate multiple locations or facilities within your organization. Additionally, we can ensure a seamless and efficient audit process across all your sites.
Even with existing safety measures, an audit can provide a fresh perspective; consequently, it can identify areas for improvement.
Simply reach out to us through our website or contact information; consequently, our team will guide you through the process.
While we cannot provide guarantees, our audits are designed to significantly enhance safety by systematically identifying and effectively mitigating potential hazards.
An audit’s benefits include accident prevention; moreover, it helps achieve regulatory compliance, cost savings, and enhanced reputation. Therefore, it is a wise investment in your organization’s future.
Elion Technologies offers a unique blend of experience; furthermore, they bring diverse expertise and personalized solutions to the table. Additionally, their commitment to a long-term safety partnership ensures that your organization’s well-being is in capable hands.
An electrical audit is a comprehensive assessment of an electrical system within a building, facility, or industrial setting to evaluate its safety, efficiency, compliance with regulations, and overall performance. Furthermore, the goal of an electrical audit is to identify potential hazards, energy inefficiencies, and opportunities for improvement. In addition, the specific items included in an electrical audit can vary depending on the type of facility and the goals of the audit; however, here are some common components typically covered:
Firstly, Safety Inspection: This involves checking for potential electrical hazards such as exposed wires, faulty outlets, improper grounding, and other safety violations. Secondly, Code Compliance: Ensuring that the electrical system adheres to relevant electrical codes and regulations set by local, national, and international standards. Thirdly, Load Analysis: Evaluating the electrical load requirements and usage patterns to ensure that the system is appropriately sized to meet the demand.
Moreover, Energy Efficiency: Identifying opportunities for energy conservation and optimization, such as recommending energy-efficient lighting, appliances, and power management strategies. Additionally, the Electrical Distribution System: Assessing the distribution of electrical power throughout the facility, including switchgear, circuit breakers, transformers, and panel boards. Furthermore, Electrical Panels and Wiring: Inspecting the condition of electrical panels, wiring, and connections for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage.
Another critical aspect is Grounding and Bonding: Checking the effectiveness of grounding and bonding systems to ensure protection against electrical faults and lightning strikes. Additionally, Voltage and Current Analysis: Measuring voltage levels, current flow, and power factor to identify any irregularities or inefficiencies. Equally important, Emergency Systems: Reviewing emergency backup systems like generators, uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), and emergency lighting.
Furthermore, Arc Flash Analysis: Assessing the potential for arc flash hazards and recommending protective measures for personnel safety. Also, Fire and Safety Systems: Verifying the integration and functionality of fire alarm systems and other safety mechanisms. In addition, Documentation and Record Keeping: Reviewing electrical drawings, maintenance records, and other documentation to ensure accuracy and completeness.
Notably, Recommendations and Action Plan: Providing a detailed report of findings, recommendations, and a prioritized action plan for addressing identified issues and improvements. Moreover, Testing and Measurement: Conducting tests, such as insulation resistance testing and ground resistance testing, to assess the integrity of the electrical system. Lastly, Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) Analysis: Identifying potential sources of electromagnetic interference that could impact sensitive equipment or systems.
It’s important to note that an electrical audit should be performed by qualified and experienced electrical engineers or professionals. Additionally, the scope and depth of the audit may vary based on factors such as the size of the facility, industry standards, and the specific goals of the audit.
The primary objective of an electrical safety audit is to ensure the safety of people, property, and operations by identifying and mitigating potential electrical hazards. Consequently, electrical safety audits are conducted to assess the effectiveness of safety measures, compliance with regulations and standards, and the overall state of the electrical system within a facility. Moreover, the specific goals of an electrical safety audit include:
Hazard Identification: To identify and evaluate potential electrical hazards that could pose a risk to personnel, equipment, and property. Additionally, this includes identifying faulty wiring, inadequate grounding, exposed conductors, and other unsafe conditions.
Personnel Safety: To assess the level of protection provided to employees, contractors, and visitors against electrical shocks, arc flashes, and other electrical incidents. Furthermore, this involves evaluating the effectiveness of safety training, personal protective equipment (PPE), and work practices.
Compliance Verification: To ensure that the facility’s electrical system complies with relevant local, national, and international electrical codes and standards. Consequently, this helps prevent legal and regulatory violations that could result in fines or other penalties.
Risk Mitigation: To implement measures that reduce the likelihood and severity of electrical accidents, fires, and disruptions. Moreover, by identifying and addressing potential risks, the audit helps prevent injuries and damage.
Equipment Integrity: To assess the condition and reliability of electrical equipment, including switches, circuit breakers, transformers, and panels. Therefore, proper maintenance and regular inspections can extend equipment lifespan and minimize downtime.
Emergency Preparedness: To evaluate the facility’s readiness to respond to electrical emergencies, such as power outages, arc flashes, and equipment failures. Additionally, this may involve reviewing emergency procedures, backup power systems, and communication protocols.
Energy Efficiency: While not the primary focus, some electrical safety audits also assess energy efficiency and recommend improvements to optimize energy consumption and reduce operating costs.
Documentation and Recordkeeping: To review and update electrical documentation, including drawings, diagrams, maintenance records, and safety procedures. Consequently, this ensures that accurate and up-to-date information is available.
Continuous Improvement: To provide recommendations for corrective actions and improvements based on audit findings. Consequently, these recommendations help organizations implement measures to enhance electrical safety over time.
Cultural Awareness: An electrical safety audit can promote a safety-conscious culture within the organization. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of safe work practices and promotes awareness of electrical risks.
Safety audits are needed for a variety of reasons across different industries and sectors. Firstly, the primary purpose of a safety audit is to assess the effectiveness of safety measures, identify potential hazards, and ensure compliance with regulations and standards. Consequently, here are some key reasons why safety audits are necessary:
Preventing Accidents and Injuries: Safety audits help identify and mitigate potential hazards before they lead to accidents or injuries. By addressing safety issues proactively, organizations can create safer work environments and protect employees, visitors, and the public.
Compliance with Regulations: Many industries are subject to specific safety regulations and standards imposed by government agencies or industry bodies. Safety audits ensure that organizations are in compliance with these regulations, reducing the risk of legal penalties and fines.
Risk Management: Safety audits provide a systematic way to assess and manage risks associated with workplace activities, processes, and equipment. By identifying and addressing risks, organizations can minimize the likelihood of accidents and the resulting financial, legal, and reputational consequences.
Continuous Improvement: Safety audits contribute to a culture of continuous improvement by identifying areas for enhancement in safety policies, procedures, and practices. Regular audits encourage organizations to evolve and adopt better safety measures over time.
Employee Morale and Productivity: When employees feel safe and confident in their work environment, their morale and job satisfaction improve. A safe workplace also boosts productivity and reduces absenteeism due to accidents or injuries.
Protecting Assets and Property: Safety audits help safeguard physical assets, equipment, and property from damage caused by accidents or safety failures. This preservation of assets contributes to cost savings and operational efficiency.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Non-compliance with safety regulations can lead to serious legal and financial consequences, including fines, lawsuits, and even shutdowns. Safety audits help organizations avoid such situations by ensuring adherence to applicable laws.
Public Image and Reputation: Organizations that prioritize safety demonstrate their commitment to the well-being of their employees and stakeholders. This positive approach to safety can enhance an organization’s public image and reputation.
Emergency Preparedness: Safety audits assess an organization’s readiness to respond to emergencies, such as fires, natural disasters, and other crises. Proper preparation can save lives and minimize damage.
Learning from Incidents: Safety audits may analyze past incidents to identify root causes and prevent similar occurrences in the future. This approach helps organizations learn from mistakes and implement corrective actions.
Contractual Requirements: Some contracts or agreements with clients, suppliers, or partners may stipulate certain safety standards that must be met. Safety audits ensure that contractual obligations are fulfilled.
Industry Best Practices: Safety audits provide an opportunity to benchmark an organization’s safety practices against industry best practices, enabling the adoption of effective strategies from other successful entities.
Electrical safety offers a wide range of benefits to individuals, organizations, and society as a whole. Consequently, by implementing effective electrical safety measures and practices, these benefits can be realized:
Prevention of Accidents and Injuries: Proper electrical safety measures significantly reduce the risk of electrical shocks, burns, and other injuries to personnel. This ensures a safer work environment and protects individuals from harm.
Preservation of Life and Health: Electrical safety practices prevent potentially fatal accidents, helping to preserve the lives and health of workers, occupants, and visitors.
Reduced Property Damage: Furthermore, electrical safety measures help prevent electrical fires and equipment damage, reducing the risk of property loss and minimizing disruptions to operations.
Compliance with Regulations: Adhering to electrical safety regulations and standards ensures legal compliance, reducing the likelihood of fines, penalties, and legal liabilities.
Cost Savings: In addition, effective electrical safety measures can lead to cost savings by minimizing accidents, injuries, property damage, downtime, and associated medical expenses.
Improved Workplace Morale: Employees who feel safe and well-protected in their work environment tend to have higher job satisfaction, which can lead to increased morale and productivity.
Enhanced Productivity: A safe work environment promotes efficient operations, reduces work-related interruptions, and supports uninterrupted production processes.
Positive Reputation: Demonstrating a commitment to electrical safety enhances an organization’s reputation and can attract clients, customers, and partners who prioritize safety.
Reduced Insurance Premiums: Organizations with strong safety practices may qualify for lower insurance premiums due to reduced risk exposure.
Business Continuity: Electrical safety measures help ensure business continuity by minimizing disruptions caused by electrical incidents, such as power outages or equipment failures.
Emergency Preparedness: Well-prepared safety protocols and procedures improve an organization’s ability to respond effectively to electrical emergencies, minimizing potential damage and risk.
Longer Equipment Lifespan: Proper maintenance and adherence to safety guidelines can extend the lifespan of electrical equipment, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
Environmental Impact: Safe electrical practices contribute to reducing the risk of electrical incidents that could lead to environmental damage or pollution.
Employee Training and Awareness: Emphasizing electrical safety promotes a culture of awareness, responsibility, and ongoing training, which benefits employees both inside and outside the workplace.
Sustainable Operations: By conserving energy, optimizing electrical usage, and preventing wasteful practices, electrical safety contributes to sustainable operations and reduced environmental impact.
Prevention of Arc Flash Incidents: Proper protective measures, such as arc flash analysis and equipment labeling, help prevent dangerous arc flash incidents that can cause severe injuries.
Mitigation of Electromagnetic Interference: Following electrical safety guidelines can help mitigate electromagnetic interference (EMI), which can impact sensitive electronic equipment and systems.
Practicing electrical safety is essential to prevent accidents, injuries, and damage. Moreover, here are five important tips to keep in mind to ensure electrical safety:
Proper Wiring and Installation:
- Ensure all electrical work is performed by qualified professionals who follow local electrical codes and regulations.
- Use the appropriate wiring and components for the intended purpose and load. Overloading circuits can lead to overheating and fires.
- Regularly inspect wiring, outlets, and switches for signs of wear, damage, or discoloration. Replace or repair as needed.
Plug and Cord Safety:
- Use quality electrical cords and plugs that are in good condition. Replace frayed or damaged cords immediately.
- Avoid overloading power strips or outlets with too many devices. Use power strips with surge protection for added safety.
- Never force a plug into an outlet, and don’t remove the grounding pin to fit a plug into a two-prong outlet.
Appliance and Equipment Safety:
- Regularly check appliances and equipment for any signs of damage or malfunction, such as strange odors, sparks, or unusual noises.
- Unplug appliances when not in use, and never touch electrical appliances or switches with wet hands.
- Keep electrical appliances away from water sources to prevent electric shock.
Outdoor Electrical Safety:
- Only use outdoor-rated extension cords and outlets for outdoor electrical devices.
- Make sure all outdoor outlets and devices are protected from rain and moisture. Use weatherproof covers as needed.
- Keep a safe distance from power lines when using ladders or other tools, and never attempt to touch or move a downed power line.
Education and Awareness:
- Educate yourself and your family members about basic electrical safety practices, including not playing with electrical outlets or cords.
- Instruct children about the dangers of electricity and the importance of not inserting objects into outlets.
- If you’re working on DIY electrical projects, make sure you have a clear understanding of what you’re doing or consult a professional.
Remember that these tips provide general guidance, and the specific electrical safety requirements can vary depending on your location, local regulations, and the nature of your electrical system. If you’re unsure about any aspect of electrical safety, it’s always best to consult a qualified electrician or professional for advice and assistance.
It helps prevent electrical accidents, fires, and compliance issues while ensuring the safety of employees and assets.
Outbound Link: Importance of Electrical Safety
Any business with electrical systems and equipment should consider an audit, especially those in high-risk industries.
Audits should be conducted regularly, typically annually or when there are significant changes to electrical systems.
Outbound Link: Audit Frequency Guidelines
The goals include identifying electrical hazards, ensuring compliance, and reducing the risk of accidents.
Audits can detect overloaded circuits, inadequate grounding, damaged wiring, and outdated equipment.
Preparation involves gathering documentation, ensuring clear access, and training employees on safety protocols.
Outbound Link: Preparing for an Audit
Auditors inspect electrical systems, review documentation, and provide recommendations for improvements.



